

If I apply pain, his body tightens towards his core.If I apply pain, his body flexes away from his core.He's saying words, but they don't make sense.No matter what I do, his eyes don't open.If "kinda" then check out that specific list and proceed.ĭO HIS EYES OPEN? (Max 4) (Eyes are easy, you're assessing eye AVPU) Do his eyes open? If yes, then score a 4. If he's a little confused, like after a concussion, but his eyes open and he has purposeful movements, then you only have to take 1 from speech. If he's totally responsive, he's E4, S5, M6. Get in the habit of looking at a patient and judging his response. Instead of writing GCS score to begin with, just start PRACTICING with using E4, S5, M6. There are 3 max points: 4) Eyes get a max of 4 points, 5) verbal gets 5 points, 6) motor gets 6 points.
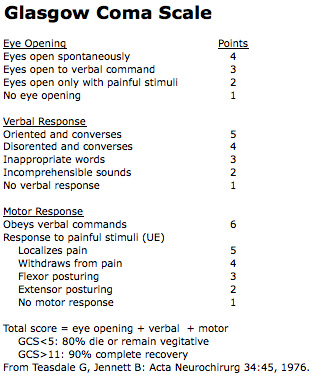
There are 3 questions: 1) Do his eyes respond? 2) Does he verbally respond? 3) Does he respond with his body? MEMORY TOOL: For GCS SCORING, Remember 1,2,3,4,5,6 (Three Questions and 3 Scores) We are assessing responsiveness because being able to react to stimuli means the brain is working. The GCS is not well validated in children and cannot-as a sole indicator-predict the need for airway interventions. The best approach in considering intubation for childhood trauma is to assess for valid indications for intubation, such as a child who cannot maintain his/her airway (determined with phonation and swallowing, not just the gag reflex).Ī separate Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale was created because young children can be harder to assess for verbal and motor function as they may not have the ability to answer your questions or follow instructions adequately. Understanding commands and cooperating with them can be compromised due to pain or immaturity. Sometimes, the "1" is omitted, and instead of using V1t, you could just see Vt since, in that case, the 1 is seen as a redundancy.Ī child's reaction to his own health crisis will not be the same as an adult's. Other common modifiers are E1c where " c" stands for closed due to swelling or damage.You can communicate that the patient is intubated with modifiers like V1t where it indicates that the patient makes no verbal sounds but it's secondary to an (endotracheal) tube.Modifiers are used to eliminate misleading scores-it's all about accuracy, especially as it pertains to outcomes. 15: The highest GCS score a patient who opens their eyes spontaneously, is oriented and alert, and obeys commands has a GCS of 15.8: The point of intubation any patient with an 8 or lower is strongly considered for intubation, as they are unlikely to maintain a patent airway.3: The lowest possible GCS this indicates a patient is wholly unresponsive.There are some GCS scores that are significant and must be memorized : You would express this as a GCS 12 = E3, V4, M5. Decorticate (flexor) posture (an abnormal posture that can include rigidity, clenched fists, legs held straight out, and arms bent inward toward the body with the wrists and fingers bend and held on the chest).ĮXAMPLE: So a patient who has scores of Eye = 3, Verbal = 4 and Motor = 5 is said to have a GCS of 12.Decerebrate (extensor) posture (an abnormal posture that can include rigidity, arms and legs held straight out, toes pointed downward, head and neck arched backward).Opens eyes in response to painful stimuli.Does not open eyes in response to anything.The sum of these scores is the Glasgow Coma Score. It is composed of 3 domains which are assessed separately and given numerical scores. The test is simple, reliable, and correlates well with outcomes following brain injury. It is often used to gauge the severity of an acute brain injury due to trauma or medical cause. The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is used to describe the level of consciousness in an individual.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
